What is dopamine?
Dopamine is a type of monoamine neurotransmitter. It’s made in your brain and acts as a chemical messenger, communicating messages between nerve cells in your brain and your brain and the rest of your body.
Dopamine also acts as a hormone. Dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine are the main catecholamines (a label based on having part of the same molecular structure). These hormones are made by your adrenal gland, a small hat-shaped gland located on top of each of your kidneys. Dopamine is also a neurohormone released by the hypothalamus in your brain.
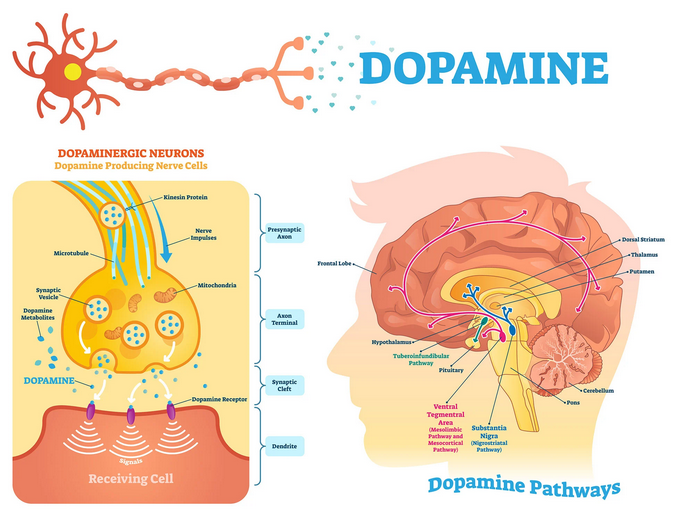 |
What’s the role of dopamine in my body?
Dopamine plays a significant role in various physiological functions in the body. As a neurotransmitter, it acts as a chemical messenger in the brain and is involved in several essential processes. Here are some key roles of dopamine in the body:
1. Mood Regulation: Dopamine is involved in regulating mood and emotional responses. It is associated with feelings of pleasure and reward, which can positively influence mood and motivation.
2. Reward and Pleasure: One of the primary roles of dopamine is in the brain's reward system. When you engage in activities that bring pleasure or reward, such as eating delicious food or engaging in enjoyable activities, dopamine is released, reinforcing these behaviors and encouraging you to repeat them.
3. Motor Control: Dopamine plays a crucial role in controlling and coordinating voluntary movements. It helps in maintaining smooth muscle movements and contributes to motor functions.
4. Learning and Memory: Dopamine is involved in cognitive processes, including learning and memory. It plays a role in reinforcing behaviors that lead to positive outcomes, which can enhance learning and memory formation.
5. Attention and Focus: Dopamine also influences attention and focus. It helps in directing and maintaining attention to important stimuli and tasks.
6. Sleep Regulation: Dopamine plays a role in the regulation of sleep-wake cycles and the sleep-wake transition.
7. Addiction and Motivation: Dopamine is closely associated with addiction and motivation. It is released in response to addictive substances or behaviors, leading to the reinforcement of these actions and driving individuals to seek them out repeatedly.
8. Stress Response: Dopamine can modulate the body's response to stress and may influence stress-related behaviors.
9. Hormone Regulation: Dopamine can also influence the release of certain hormones, affecting various physiological processes.
Dopamine is a complex neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions, and its proper regulation is essential for overall well-being and optimal brain function. Imbalances in dopamine levels can be associated with various neurological and psychiatric conditions, such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and addiction. However, dopamine's functions are interconnected with other neurotransmitters and brain systems, contributing to the complex and intricate workings of the brain and the body.
How does dopamine make someone feel happy?
You're absolutely right! Dopamine
is a multifaceted neurotransmitter and hormone that plays a vital role in various
body functions. As a neurotransmitter, it is involved in numerous processes in
the brain, influencing movement, memory, reward and motivation, behavior,
cognition, attention, sleep, mood, learning, and lactation.
As a hormone, dopamine is released into the bloodstream and contributes to several physiological responses in the body:
1. Fight-or-flight response: Dopamine plays a small role in the "fight-or-flight" response, which is the body's reaction to perceived or real stress or danger. It is part of the complex stress response system in the body.
2. Cardiovascular effects: Dopamine can cause blood vessels to relax (vasodilation) at low doses and constrict (vasoconstriction) at high doses. This can influence blood pressure regulation.
3. Renal effects: Dopamine can increase the excretion of sodium and urine from the body, which helps in maintaining fluid balance and blood pressure.
4. Pancreatic effects: Dopamine reduces insulin production in the pancreas, which is involved in regulating blood sugar levels.
5. Gastrointestinal effects: Dopamine slows down gastrointestinal (GI) content movement and has protective effects on the GI lining.
6. Immune system effects: Dopamine can reduce the activity of lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cells involved in the immune response.
The diverse roles of dopamine highlight its importance in maintaining various physiological functions and its impact on overall health and well-being. Imbalances in dopamine levels can have significant implications for both physical and mental health and may be associated with various medical conditions. It is a complex and essential chemical messenger in the body, and its proper regulation is crucial for the body's optimal functioning.
How might I feel if I have the right amount of dopamine?
Exactly! When dopamine levels are balanced and within the optimal range, you are likely to experience the following positive feelings and states:
1. Happy: Dopamine is often associated with feelings of pleasure and happiness. Having the right balance of dopamine can contribute to an overall sense of well-being and contentment, leading to feelings of happiness.
2. Motivated: Dopamine plays a key role in motivation and goal-directed behavior. When dopamine levels are in the appropriate range, you are more likely to feel motivated and driven to pursue your goals and aspirations.
3. Alert: Dopamine is involved in attention and focus. With balanced dopamine levels, you are more likely to feel alert and attentive, allowing you to stay focused on tasks and activities.
4. Focused: Proper dopamine levels can enhance cognitive function and mental clarity, which can lead to improved focus and concentration.
These positive effects of dopamine on mood, motivation, attention, and focus are essential for overall well-being and optimal brain function. It's important to note that dopamine is just one of many neurotransmitters and factors that influence emotions and behaviors, and its effects are interconnected with other brain systems. Maintaining a healthy and balanced lifestyle, including regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and a balanced diet, can contribute to maintaining the optimal balance of dopamine and overall brain health. If you have concerns about your mood, motivation, or focus, it's advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare professional to explore any underlying issues and receive appropriate support.
How might I feel if I have a low dopamine level?
If you have low dopamine levels, you may experience a range of physical, emotional, and cognitive symptoms. Dopamine is a crucial neurotransmitter involved in various functions, and its deficiency can have significant effects on your overall well-being. Some common signs and symptoms of low dopamine levels include:
1. Low Mood: Dopamine is often referred to as the "feel-good" neurotransmitter. A deficiency in dopamine can lead to feelings of sadness, depression, or a general lack of pleasure and interest in activities you used to enjoy.
2. Lack of Motivation: Dopamine plays a key role in motivation and goal-directed behavior. Low dopamine levels may lead to a decreased desire to engage in activities or pursue goals, making it challenging to find the drive to complete tasks.
3. Fatigue and Low Energy: Dopamine is involved in the brain's regulation of energy levels. Low dopamine levels can contribute to feelings of fatigue, lethargy, and a lack of energy.
4. Cognitive Difficulties: Dopamine is important for cognitive function, including memory, attention, and problem-solving. With low dopamine levels, you may experience difficulties in concentration, memory lapses, and reduced mental clarity.
5. Sleep Problems: Dopamine plays a role in regulating sleep-wake cycles. Low dopamine levels can lead to disturbances in sleep patterns, such as difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
6. Weight Changes: Dopamine can influence appetite and eating behavior. Low dopamine levels may contribute to changes in appetite, potentially leading to weight loss or weight gain.
7. Reduced Libido: Dopamine is involved in sexual desire and arousal. Low dopamine levels can lead to a decrease in libido and interest in sexual activities.
8. Restlessness: Dopamine helps regulate movement and coordination. With low dopamine levels, you may experience restlessness, muscle stiffness, or difficulties in fine motor control.
It's important to remember that dopamine deficiency is just one of many possible factors that can contribute to these symptoms. Other medical, psychological, or lifestyle factors could also play a role. If you are experiencing persistent or concerning symptoms, it's crucial to seek evaluation and guidance from a healthcare professional. They can assess your overall health, determine if dopamine levels are a contributing factor, and recommend appropriate interventions or treatments to address any underlying issues.
How might I feel if I have a high dopamine level?
If you have high dopamine levels, you may experience a range of physical, emotional, and behavioral effects. While dopamine is essential for mood regulation, motivation, and pleasure, excessively high levels can lead to various symptoms and potential imbalances in the brains functioning. Some common signs and symptoms of high dopamine levels include:
1. Euphoria: Excess dopamine can lead to feelings of intense pleasure and euphoria. This can result from activities or substances that trigger an abnormally large release of dopamine in the brain's reward system.
2. Increased Energy: High dopamine levels can lead to a surge in energy and feelings of restlessness or hyperactivity.
3. Agitation and Anxiety: Excess dopamine can sometimes be associated with feelings of agitation, anxiety, or even paranoia.
4. Impulsivity: High dopamine levels may lead to increased impulsivity and risky behaviors.
5. Difficulty Sleeping: Elevated dopamine levels can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
6. Loss of Appetite: High dopamine levels can suppress appetite, leading to a reduced desire for food.
7. Mania: In extreme cases, excessively high dopamine levels can contribute to manic episodes in individuals with bipolar disorder.
8. Tics or Involuntary Movements: In rare instances, elevated dopamine levels can be associated with tics or involuntary movements.
It's important to note that the effects of high dopamine levels can vary from person to person and may be influenced by other factors, such as individual brain chemistry, genetics, and overall health. Additionally, high dopamine levels can result from various causes, including certain medications, drug use, or medical conditions.
If you suspect you have high dopamine levels or experience symptoms that concern you, it's crucial to seek evaluation and guidance from a healthcare professional. They can help identify potential underlying causes and provide appropriate recommendations or treatments to restore a healthy balance in the brain's dopamine levels.
What health conditions are associated with high or low dopamine levels?
Both high and low dopamine levels can be associated with various health conditions. Dopamine plays a complex role in the brain and the body, and imbalances in its levels can have significant effects on physical and mental health. Here are some health conditions associated with high or low dopamine levels:
Health Conditions Associated with High Dopamine Levels:
1. Mania in Bipolar Disorder: During manic episodes in bipolar disorder, there can be a significant increase in dopamine levels, contributing to the characteristic symptoms of heightened mood, increased energy, and impulsivity.
2. Psychosis and Schizophrenia: Excessive dopamine activity in certain brain regions has been linked to psychotic symptoms, such as hallucinations and delusions, often seen in schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders.
3. Substance Use Disorders: Drugs and substances that lead to a rapid release of dopamine in the brain's reward system can lead to addiction and substance use disorders.
4. Hyperactivity and Restlessness: High dopamine levels can lead to restlessness, hyperactivity, and difficulties in maintaining attention and focus.
Health Conditions Associated with Low Dopamine Levels:
1. Depression: Low dopamine levels have been associated with depression and a reduced ability to experience pleasure or motivation.
2. Parkinson's Disease: Parkinson's disease is characterized by the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, leading to movement difficulties, tremors, and other motor symptoms.
3. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): ADHD has been linked to imbalances in dopamine levels, contributing to symptoms such as inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
4. Anhedonia: Anhedonia is the inability to experience pleasure or interest in previously enjoyable activities, and it is often associated with low dopamine levels.
5. Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): RLS is a condition characterized by uncomfortable sensations in the legs, often relieved by movement. It is thought to involve dopamine dysfunction in the brain.
6. Schizophrenia: While excess dopamine activity is associated with some symptoms of schizophrenia, certain symptoms of the disorder may also be related to low dopamine levels in specific brain regions.
It's important to note that dopamine is just one of many neurotransmitters and factors that influence these conditions. The relationship between dopamine and these health conditions is complex and involves interactions with other neurotransmitters, genetics, and environmental factors.
If you suspect that you may have imbalances in dopamine levels or are experiencing symptoms associated with these health conditions, it's essential to seek evaluation and support from a healthcare professional. They can provide a thorough assessment, make an accurate diagnosis, and develop a personalized treatment plan to address any underlying issues.
How can I improve my dopamine levels in a natural way?
You can naturally support healthy dopamine levels through various lifestyle choices and practices. Here are some strategies to help improve and maintain dopamine levels naturally:
1. Diet: Eat a well-balanced diet that includes sources of important dopamine precursors, such as tyrosine and phenylalanine. Foods rich in these amino acids include lean proteins (chicken, turkey, and fish), dairy products, soy products, eggs, nuts, and seeds. Additionally, ensure you have enough vitamins and minerals, such as iron, magnesium, and B-vitamins, which are essential for dopamine synthesis.
2. Exercise: Regular physical activity can boost dopamine levels and promote overall brain health. Aim for moderate aerobic exercise, such as walking, jogging, or dancing, for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
3. Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep, as lack of sleep can negatively impact dopamine regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep each night.
4. Stress Management: Chronic stress can deplete dopamine levels. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or spending time in nature.
5. Social Connections: Engage in positive social interactions, as social bonding and connection can increase dopamine release.
6. Mindful Eating: Savor your meals and eat mindfully, appreciating the flavors and textures. This can enhance the reward response and dopamine release associated with eating.
7. Achievement and Goal Setting: Set achievable goals and work towards them. The sense of accomplishment and progress can positively impact dopamine levels.
8. Reward Yourself: Reward yourself for completing tasks or achieving goals. Positive reinforcement can stimulate dopamine release.
9. Hobbies and Interests: Engage in activities you genuinely enjoy, such as hobbies, sports, or creative pursuits. These activities can naturally boost dopamine levels.
10. Limit Stimulants: Reduce or avoid excessive caffeine, as it can lead to dopamine fluctuations and tolerance.
11. Limit Addictive Substances: Avoid or minimize the use of drugs, alcohol, and other addictive substances, as they can disrupt dopamine balance.
Remember that dopamine levels are influenced by various factors, and individual responses may vary. If you have concerns about your mood, motivation, or well-being, or suspect you may have imbalances in dopamine levels, consider consulting a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized guidance and support to optimize your brain health and overall well-being.









0 Comments